Today, we are going to discuss Variables and its type.
It is a very important question in an examination/interviews and these concepts are very useful when it comes to writing code.
Variables - " A variable is a container that holds values that are used in a program ".
In Java, three types of variable...
- Local Variable
- Instance Variable
- Static Variable
# Local Variable
- A variable which declares inside a block.
Ques - What is block?
Ans - Except class, anything has " { } " open and close curly braces are called block.
For Example - methods, loops etc.
- Local Variable is not accessible outside the block, where it is declared.
- Life of the local variable is the life of the block.
- No default value for Local Variables.
- Local Variable value must be explicitly initialized before its use.
Now, There are two types of the variable which can be initialized inside the class.
- Instance Variable
- Static Variable
# Instance Variable
- A variable which is directly declared inside the class is called instance variable.
- Instance variable is used to store object specific properties/values.
- Each object may have its own value for that property ---- for this kind of property we should use instance variable to store values.
# Static Variable
- A variable which is directly declared inside the class with the static keyword is called static variable.
- only one copy of in memory for static variables and all objects share its value.
- Life of a static variable is the life of a class.
- memory is assigned to static variables when the class is loaded in JVM.
- defaults values are assigned to static variables.
# Example:-
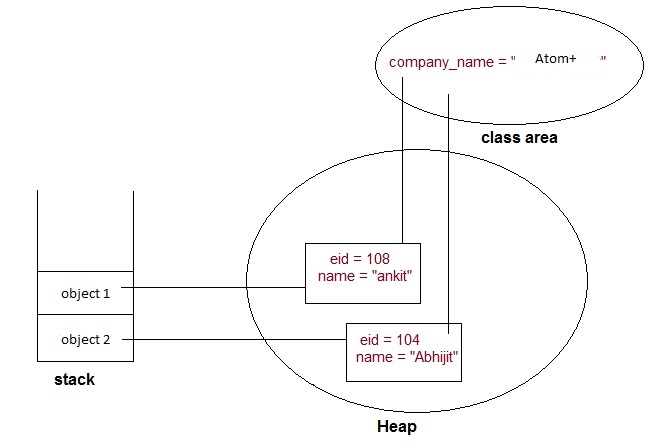
Suppose there is 1000 employ in a company (let's say Atom+ Company ), now all employs has its own employ ID and name but all employ has the same company name.
For object specific properties/values --- we can use Instance variables. -- like name & employID.
For Common object properties --- we can use static variables. -- like Company Name.